Anaerobic cellular respiration generates ATP when insufficient oxygen is available for aerobic respiration.
Anaerobic respiration takes place afterglycolysis。This process differs among species, and in mammals it is calledlactic acid fermentation。乳酸发酵不需要氧气proceed, although it can occur in its presence. Duringlactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is converted into lactic acid and the NADH produced during glycolysis is recycled. The net release of energy comes from glycolysis in the form of 2 ATP molecules.
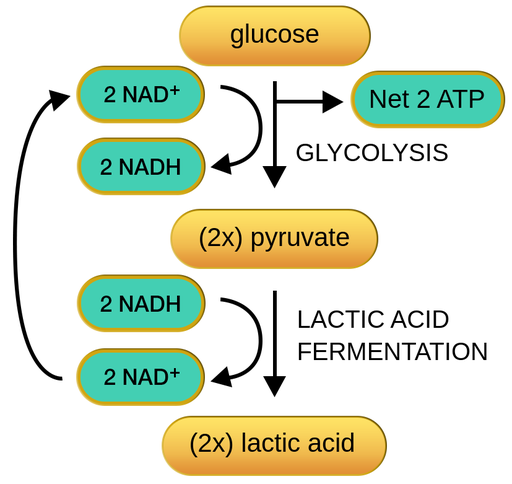
Overview of anaerobic cellular respiration in mammals.